Medical state structures and commercial organizations have daily access to a large amount of personal data. The issue of information security is particularly acute in current conditions, when it is imperative to ensure data storage.
The introduction of cutting-edge technologies in the field of healthcare increases the likelihood of information leakage and theft. Today we will discuss the main issues connected with health data protection:
- How to safeguard data
- Prospects for information security
- Methods of strengthening it
- Data protection legislation
Learn how to simplify your practice workflow and free up more time for patients with Medesk.
Open the detailed description >>Specifics Of Data Protection In Medical Institutions
Data in medical organizations often fall into the category of medical confidentiality. These include personal information about employees and customers. Disclosure of such health information can have minor consequences, such as low retention rates. Moreover, hackers use stolen data for fraudulent purposes, sell it on the black market or blackmail organizations that leaked it.
The specifics of working with medical information determine the scope of work in terms of information security:
- All information is at the complete disposal of the patient
- The processing of documents must be carried out promptly
- Different parts of medical information are processed by different specialists, including laboratory assistants, nurses, doctors, registrars
- The division of information into personal and statistical data, further information about the course of treatment
- The rules of interaction between medical staff, patients and trusted persons have not been established.
To address these complex data protection challenges, many healthcare organizations are turning to healthcare contract review software. These AI-powered tools can help ensure compliance with data protection regulations across all contractual agreements, streamlining the process of managing and reviewing healthcare-specific contracts.
What is personal data in medicine?
Simple personal data includes the following information about patients and clinic staff:
- Last name, first name, patronymic
- Date and place of birth
- Anthropometric indicators (height, weight)
- Photos
- Place of residence, contact phone numbers.
Medesk helps automate scheduling and record-keeping, allowing you to recreate an individual approach to each patient, providing them with maximum attention.
Learn more >>Personal data in public health institutions is added to the list of items in a special category. The information in this section describes the patient's health status, his reasons for seeking medical help, and the features of his treatment. The term "medical confidentiality" refers to this special information.
Working with patient information
It is forbidden to disclose medical secrets even after the patient's death. At the same time, clinics are required to store data on the health of each person who applies in the form of a patient card. The problem of information leakage may arise at every stage of the interaction of medical institution staff with personal patient cards.
The workflow of data controllers consists of the following stages:
- Collecting and recording information
- Systematization of the received data
- Storing information in a database
- Clarification of details (if necessary)
- Destruction of irrelevant information.
Protection should be provided at every contact of personnel with the medical records of patients. It is difficult to achieve this in medical institutions.
New Technologies and Data Protection
The number of tools that allow tracking patient status data has increased dramatically over the past few years. This has become possible thanks to the development of cloud technologies, mobile devices and the ability to store arrays of data online.
Mobile medtech apps have also significantly improved the quality of patient care. Users have the opportunity to learn more information about their bodies, and take better care of their health. At the same time, medical organizations save money. But they should understand how and where the information generated by gadgets is stored.
If a clinician runs a social media account, he must comply with HIPAA regulations and keep in mind the challenges of misinformation, cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
The development of these technologies also stimulates the exchange of medical data for clinical research. Patients and their family members can consent to sending information for subsequent tests. Doctors can exchange data, for example, for genetic studies. But the healthcare industry has yet to earn the trust of patients.
Vulnerability of Information Systems In Medical Institutions
There is a possibility of the following information security violations:
- Unauthorized access to information, violation of confidentiality
- Loss of information caused by destruction of the data carrier or erasure of data
- Making changes with direct access to the database or through the system interface
- Functional failure related to obtaining access to information
- Getting access to the database
- Incorrect functioning of the information system due to unauthorized modification of modules.
There are still ways to comply with the legal obligation of data sharing and protection. Check out these tips.
Patient Data Protection Tips
Patient sensitive data must be kept secure to protect patients' privacy and to comply with legal requirements.
There are several steps that health professionals can take to protect patient data.
#1. Implement a security management system
This involves creating policies, procedures, and guidelines for data protection, and training staff on how to handle sensitive information securely. A security management system is a set of policies, procedures, and guidelines that are put in place to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of patient data. Utilizing a feature-rich VPN can significantly boost your security framework by safeguarding data exchanges and ensuring that sensitive information remains private and protected.
Discover more about the essential features of Medesk and claim your free access today!
Explore now >>This involves creating retention policies and procedures that outline how data should be handled, stored, and protected. These policies and procedures should be in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
#2. Encrypt data
This involves converting data into a code so that it can only be read by authorized individuals.
First thing is to identify which data needs to be encrypted. Typically, this includes personal health information (PHI) and personal identifying information (PII).
There are several encryption methods available, including symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption, and hashing. Each method has its own set of strengths and weaknesses, and the most appropriate method will depend on the specific needs of the organization.
It's important to note that encryption should be part of a comprehensive security strategy. This strategy should be combined with other security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls.
#3. Back up data regularly
This helps to ensure that sensitive information is not lost in the event of a data breach, system failure, or other disaster.
Generally, encrypted data, such as PHI and PII, must be backed up. It’s wise to set up a backup schedule to ensure that data is backed up frequently and at appropriate intervals. You can use full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups depending on your health records needs.
#4. Monitor and log access to data
The process involves putting in place technical controls such as intrusion detection systems, security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and access controls to monitor and log access to data.
Your task is to respond to any suspicious activity or unauthorized access promptly, test the security of the systems, and conduct regular vulnerability assessments.
#5. Implement access controls
This step is aimed at limiting who can access patient data and what they can do with it. Here we talk about implementing authentication methods, such as user IDs and passwords, smart cards, or biometrics, to ensure that only authorized individuals can access patient data. Implementing robust security measures doesn't just apply to digital systems. It’s essential to secure physical installations as well. Ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive areas can further protect patient data and enhance overall security. Companies like Mammoth Security specialize in high-quality security system installations, helping facilities maintain a high level of safety and compliance. Additionally, an overview of SCIM provisioning can be useful for understanding how to automate the process of managing user identities in cloud-based applications and services.
Implementing authorization and access controls on all systems also contributes to sharing information safely.
#6. Conduct regular risk assessments
Conducting regular risk assessments is an effective step in protecting patient data in healthcare. Risk assessments help to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats to patient data and to develop strategies to mitigate or eliminate them.
Regular assessments help to identify the above-mentioned risks of data breaches and unauthorized access.
#7. Implement an incident response plan
An incident response plan is a set of procedures and processes that are put in place to respond to and manage data breaches, system failures, or other security incidents.
For the plan to work you must designate a team responsible for responding to and managing security incidents. Communication between the members of the team and all other parties involved includes incident response exercises to test the incident response plan and identify any areas for improvement.
Health and social care workers should review and update the incident response plan to ensure that it remains current and that any new risks are identified and addressed.
#8. Comply with legal and regulatory requirements
This includes complying with healthcare data protection laws and public authority regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the US and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the EU.
It came into effect on May 25th, 2018, replacing the Data Protection Act 1998. It is also known as the Data Protection Act 2018.
The essence of GDPR is to give EU citizens more control over their personal data. Furthermore, it seeks to simplify the regulatory environment for international business by unifying EU regulations.
By taking these steps, healthcare organizations can help to protect patient data and maintain the trust of their patients.
GDPR also introduced enhanced requirements for data security, data processors and data controllers, increased fines and sanctions, and the appointment of Data Protection Officers.
Health Information Systems For Information Governance and Data Portability
The use of modern information systems takes care services to a new level of convenience and protection. Today, three effective tools are used for the secure processing of personal data in hospitals:
- Special applications with local or network storage
- Practice management software operating within a specific medical center
- Cloud programs for collecting and storing information.
Each of the presented information systems has its own algorithm for ensuring the security of personal information.
The Medesk platform provides information security due to a fragmented architecture of construction, which splits a common information array into cells. You can set different access rights for each employee.
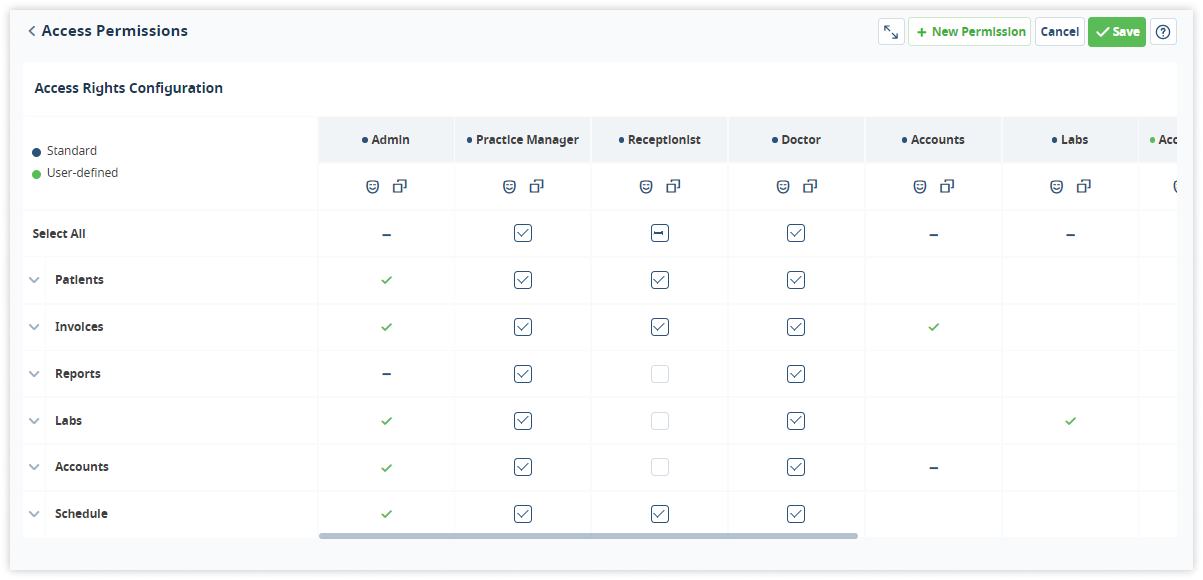
When using the listed technologies, the risk of hacking and theft of personal data is minimal. However, it is wise to restrict access to working with databases to outsiders.
To do this, the clinic's management should take a set of measures, including subject access requests, round-the-clock video surveillance, and a multi-level password system. This will help to avoid deliberate theft of the personal information of patients and employees.
In the fight for the protection of personal data in medicine, do not forget to regularly familiarize clinic staff with the provisions of current legislation. Information is often leaked unknowingly, as a result of the inattentive attitude of doctors and junior medical staff to the preservation of medical secrecy.
To Sum It Up
In conclusion, data protection in medical institutions is crucial due to the sensitive nature of personal health information. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies to any company that processes or holds personal data of EU citizens.
Medical providers need to implement strong data protection measures such as access controls, encryption, regular backups, incident response plans, regular risk assessments, employee training and appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to ensure compliance with GDPR. They should also provide transparency and give patients the right to access, rectify, erase, and object to the processing of their personal data.


